
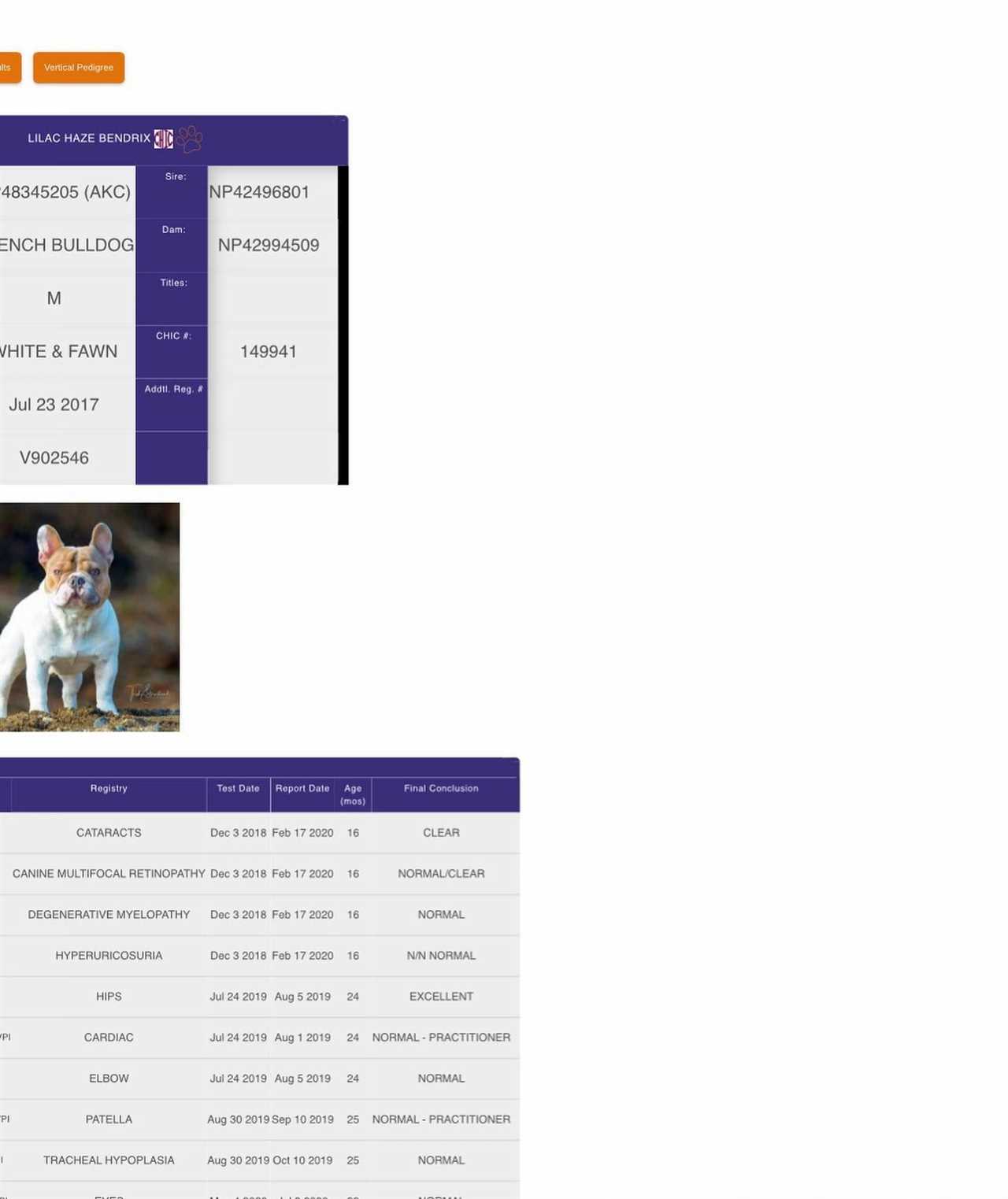
The French Bulldog is a popular breed known for its distinctive appearance and charming personality. One of the most fascinating aspects of this breed is its wide range of coat colors. French Bulldogs can come in a variety of shades, from classic fawn and brindle to rare and unique colors like blue, chocolate, and lilac.
To better understand the genetics behind these different coat colors, many breeders and enthusiasts have turned to DNA testing. By analyzing the DNA of French Bulldogs, researchers have been able to create a comprehensive color chart that helps identify and predict the possible coat colors of these adorable dogs.
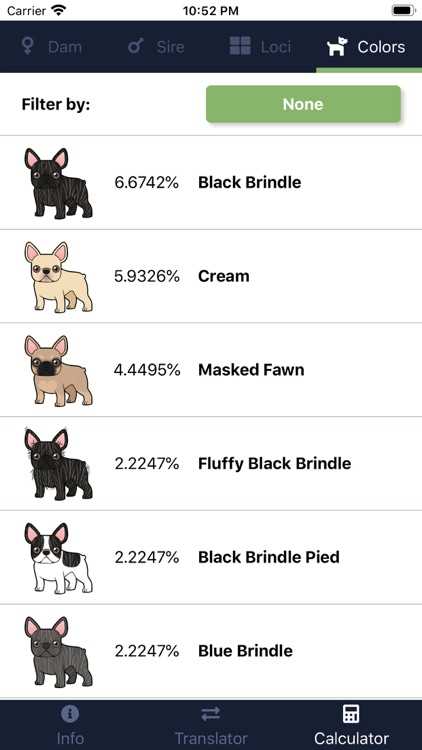
The French Bulldog DNA color chart categorizes the coat colors into different groups based on the genes responsible for each color. Some of the most common colors include fawn, brindle, pied, and black. Each color group is further divided into different shades and patterns, providing a detailed guide to understanding the genetics of French Bulldog coat colors.
Understanding the DNA color chart can be incredibly helpful for breeders who want to produce specific coat colors or avoid certain genetic combinations. It also allows French Bulldog owners and enthusiasts to gain a deeper appreciation for the genetics behind their beloved pets’ unique appearances.
Whether you are a breeder, owner, or simply a fan of French Bulldogs, exploring the DNA color chart can be a fascinating journey into the world of genetics and coat colors. It allows us to appreciate the diversity and beauty of this breed while also helping us make informed decisions when it comes to breeding and caring for French Bulldogs.
Why DNA Determines Coat Color
The coat color of a French Bulldog is determined by its DNA. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material found in cells that carries the instructions for the development and functioning of an organism. In the case of coat color, specific genes and genetic markers play a crucial role in determining the pigmentation of a French Bulldog’s fur.
Coat color is a complex trait that is influenced by multiple genes. These genes interact with each other and with environmental factors to produce a wide range of coat colors and patterns. Understanding the genetic basis of coat color in French Bulldogs is important for breeders and enthusiasts who want to selectively breed for specific colors or avoid certain genetic disorders associated with certain coat colors.
Genes and Genetic Markers

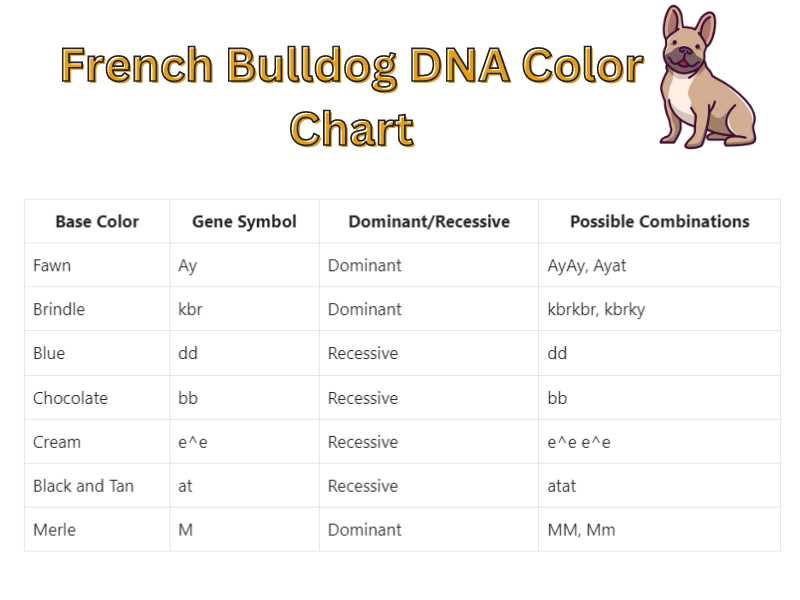
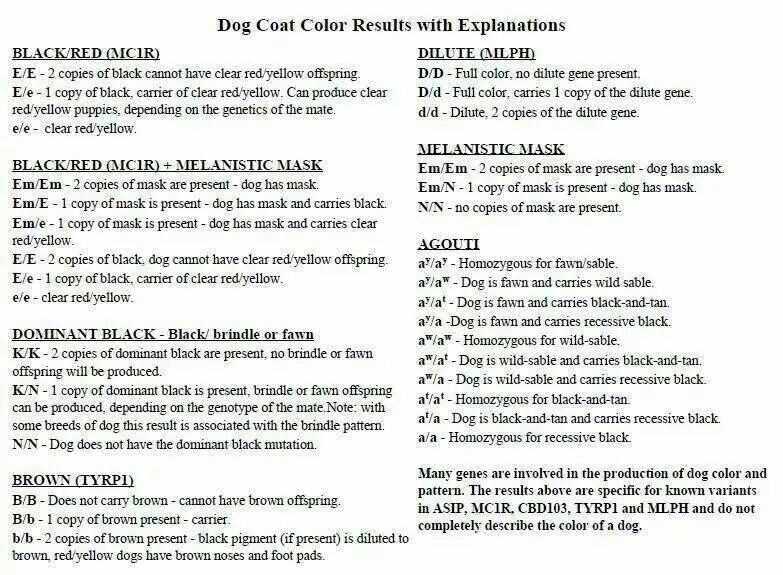
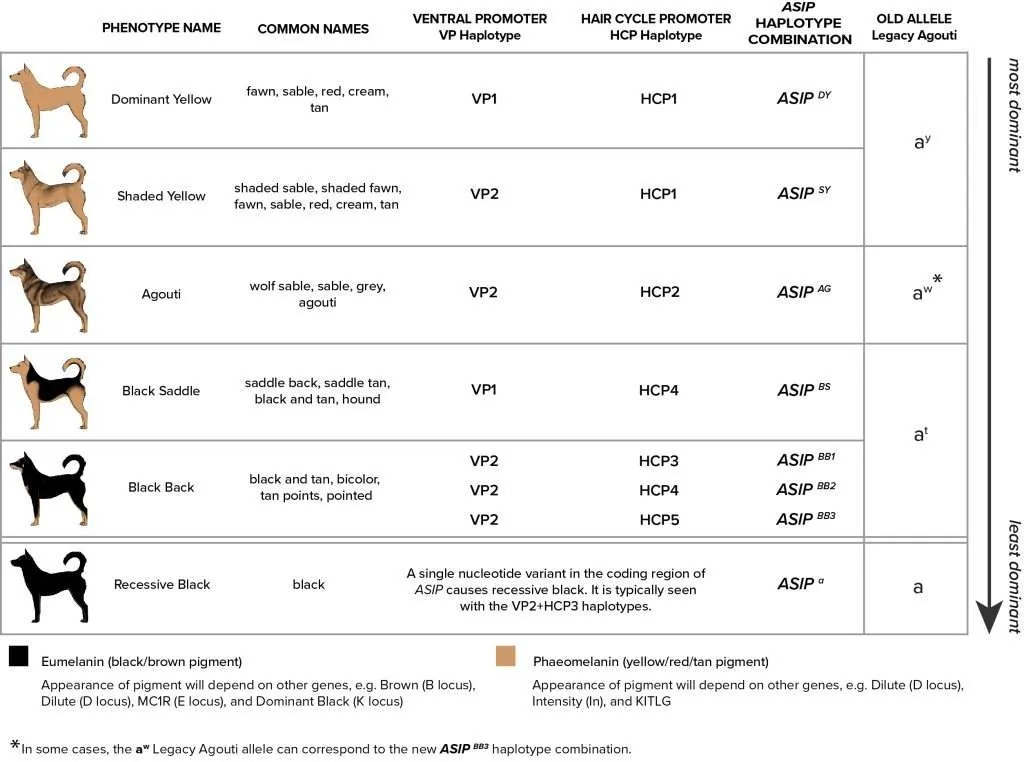
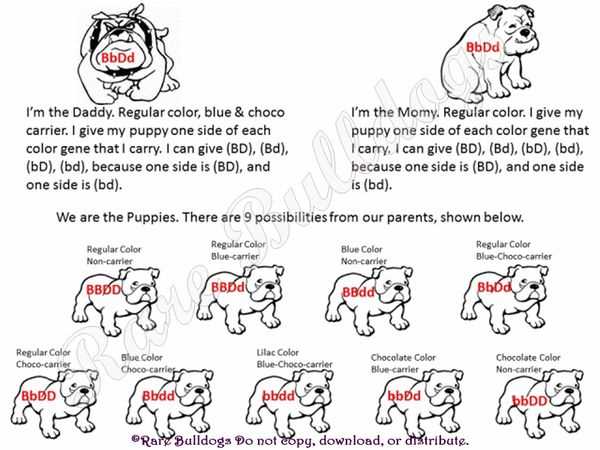
There are several genes and genetic markers that are known to influence coat color in French Bulldogs. One of the most well-known genes is the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene, which controls the production of melanin, the pigment that gives color to the hair, skin, and eyes. Variations in the MC1R gene can result in different coat colors, such as black, fawn, brindle, or pied.
In addition to the MC1R gene, other genes and genetic markers, such as the agouti signaling protein (ASIP) gene and the beta-defensin 103 (CBD103) gene, also play a role in determining coat color. These genes interact with the MC1R gene and other genes to produce specific coat color patterns and variations.
Testing for Coat Color Genes

Genetic testing can be used to determine the coat color genes present in a French Bulldog. This involves taking a DNA sample, usually through a cheek swab or blood sample, and analyzing it in a laboratory. The results of the genetic test can provide valuable information about the dog’s coat color genetics, allowing breeders to make informed decisions about breeding strategies and potential color outcomes.
Genetic testing can also help identify carriers of certain genetic disorders associated with specific coat colors. For example, some coat color variations, such as blue or chocolate, are associated with a higher risk of certain health conditions. By identifying carriers of these variations, breeders can make informed decisions to reduce the risk of passing on these disorders to future generations.
| Coat Color | Genes Involved |
|---|---|
| Black | MC1R (E/E or E/e) |
| Fawn | MC1R (e/e) |
| Brindle | MC1R (E/E or E/e) + ASIP |
| Pied | MC1R (E/E or E/e) + CBD103 |
Understanding the genetic basis of coat color in French Bulldogs can also help with the identification of potential color changes over time. Some coat colors, such as brindle, may change or fade as the dog matures. By understanding the underlying genetic factors, breeders and owners can better predict and understand these changes.
The Different Coat Colors
The French Bulldog breed is known for its wide range of coat colors, which adds to their charm and popularity. Here are some of the different coat colors that can be found in French Bulldogs:
1. Fawn
Fawn is one of the most common coat colors in French Bulldogs. It ranges from a light tan to a deep reddish-brown shade. The coat is usually solid and may have a slight variation in color on the ears and face.
2. Brindle
Brindle is another popular coat color in French Bulldogs. It is characterized by a pattern of dark stripes on a lighter background color. The stripes can be black, dark brown, or a combination of both. Brindle French Bulldogs can have a variety of base colors, including fawn, cream, or even blue.
3. Pied
Pied French Bulldogs have a predominantly white coat with patches of any other color. The patches can be of any size and can appear on different parts of the body, including the head, ears, and body. The white color is usually the dominant color in pied French Bulldogs.
4. Black
Black French Bulldogs have a solid black coat without any other color markings. This coat color is less common than fawn or brindle but is still highly sought after by many Frenchie enthusiasts.
5. Blue
Blue French Bulldogs have a coat that appears bluish-gray. This color is the result of a dilution gene that affects the production of pigment in the hair shaft. Blue French Bulldogs can have various shades of gray, ranging from light silver to a darker steel blue.
6. Cream
Cream French Bulldogs have a coat color that is light in shade, resembling the color of cream. This color is often seen in combination with other colors, such as fawn or brindle. Cream French Bulldogs can have a solid coat or may have lighter patches on their body.
7. Chocolate
Chocolate French Bulldogs have a coat color that is rich brown in shade. This color is the result of a specific gene that affects the production of pigment. Chocolate French Bulldogs can have various shades of brown, ranging from light milk chocolate to a darker chocolate brown.
These are just a few examples of the different coat colors that can be found in French Bulldogs. Each coat color has its own unique charm and appeal, making French Bulldogs a visually diverse and fascinating breed.
Genetic Markers and Testing
Genetic markers are specific sections of DNA that can be used to identify certain traits or characteristics. In the case of French Bulldogs, genetic markers are used to determine coat color. These markers are like signposts along the DNA strand that can indicate the presence or absence of certain genes responsible for coat color.
To test for coat color in French Bulldogs, a DNA sample is collected, usually through a simple cheek swab or blood sample. This sample is then sent to a laboratory where it is analyzed using a process called genotyping. Genotyping allows scientists to identify the specific genetic markers associated with coat color.
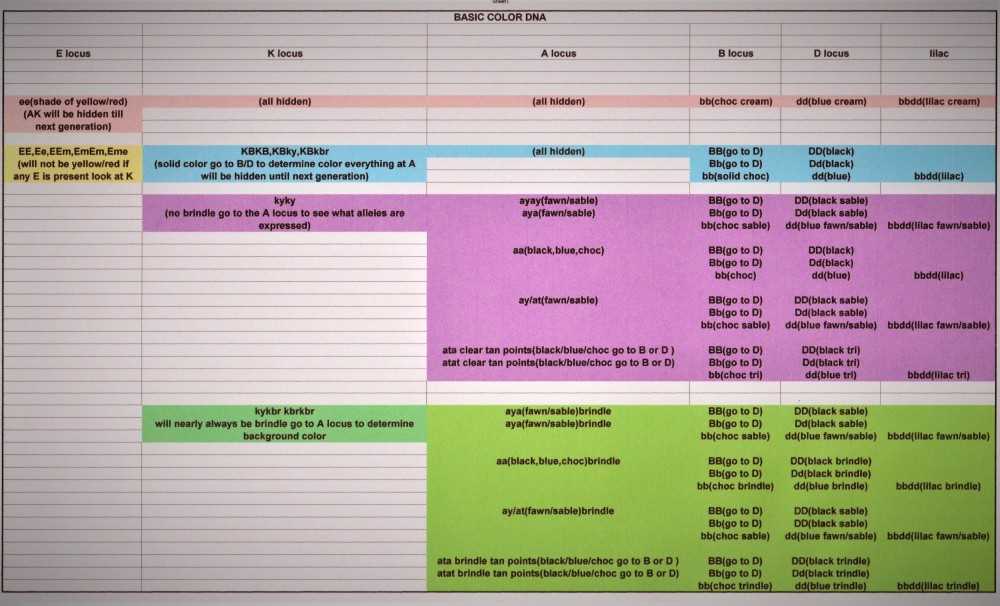
There are several genetic markers that have been identified in French Bulldogs, each corresponding to a different coat color. For example, the A locus marker determines whether a dog has a dominant black or recessive black coat. The E locus marker determines whether a dog has a solid coat or a patterned coat.
Understanding the Results
Once the genetic markers have been analyzed, the results are typically presented in a report or certificate. This report will outline the specific genetic markers that were tested and the corresponding coat color that each marker represents.
It’s important to note that coat color in French Bulldogs is not determined by a single gene, but rather by a combination of genes and genetic markers. This means that the presence of certain markers does not guarantee a specific coat color, but rather increases the likelihood of that color being expressed.
Benefits of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing for coat color in French Bulldogs can be beneficial for both breeders and owners. For breeders, genetic testing can help them make informed decisions when selecting breeding pairs to achieve desired coat colors. It can also help them avoid breeding dogs that may carry genetic markers for coat colors that are undesirable or associated with health issues.
For owners, genetic testing can provide valuable information about their dog’s coat color and potential color changes over time. It can also help them understand the inheritance patterns of coat color and make informed decisions about breeding or genetic health.
Breeding Strategies for Desired Colors
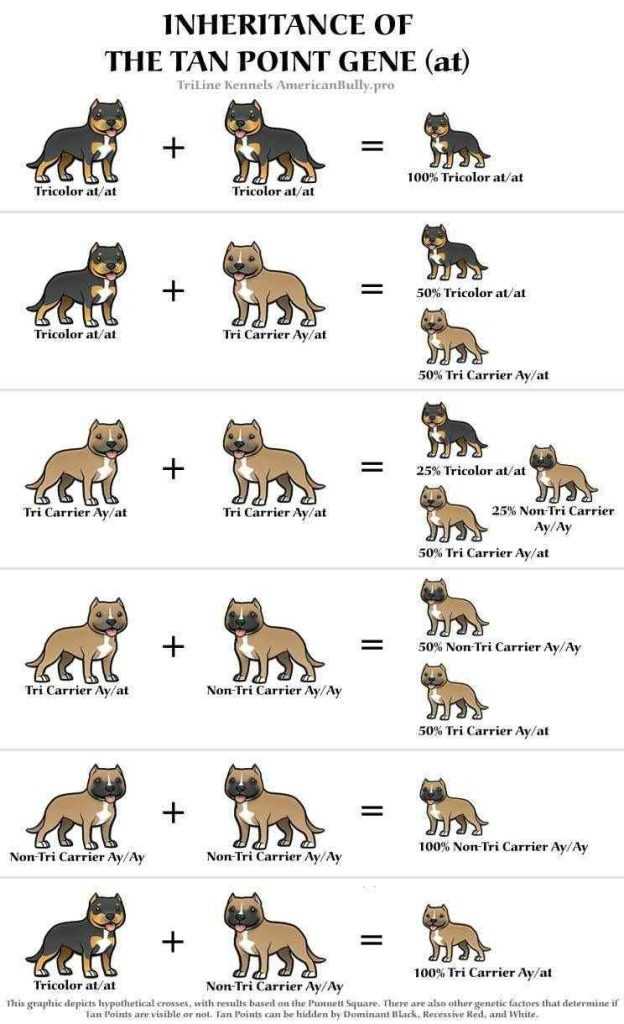
Breeding French Bulldogs for desired coat colors requires careful planning and consideration of genetic factors. Here are some strategies breeders can employ to achieve specific color outcomes:
1. Understand the Genetics: Familiarize yourself with the basics of coat color genetics in French Bulldogs. Learn about the different alleles and genetic markers that influence coat color inheritance.
2. Select Parent Dogs with Desired Colors: Choose parent dogs that possess the desired coat colors you wish to breed. Ensure that both dogs carry the necessary genetic markers for the desired color.
3. Consider Carrier Dogs: Some coat colors are recessive and may not be visibly expressed in a dog’s phenotype. However, carriers of these recessive genes can still pass them on to their offspring. Identify carrier dogs and use them strategically in breeding programs to increase the chances of producing desired colors.
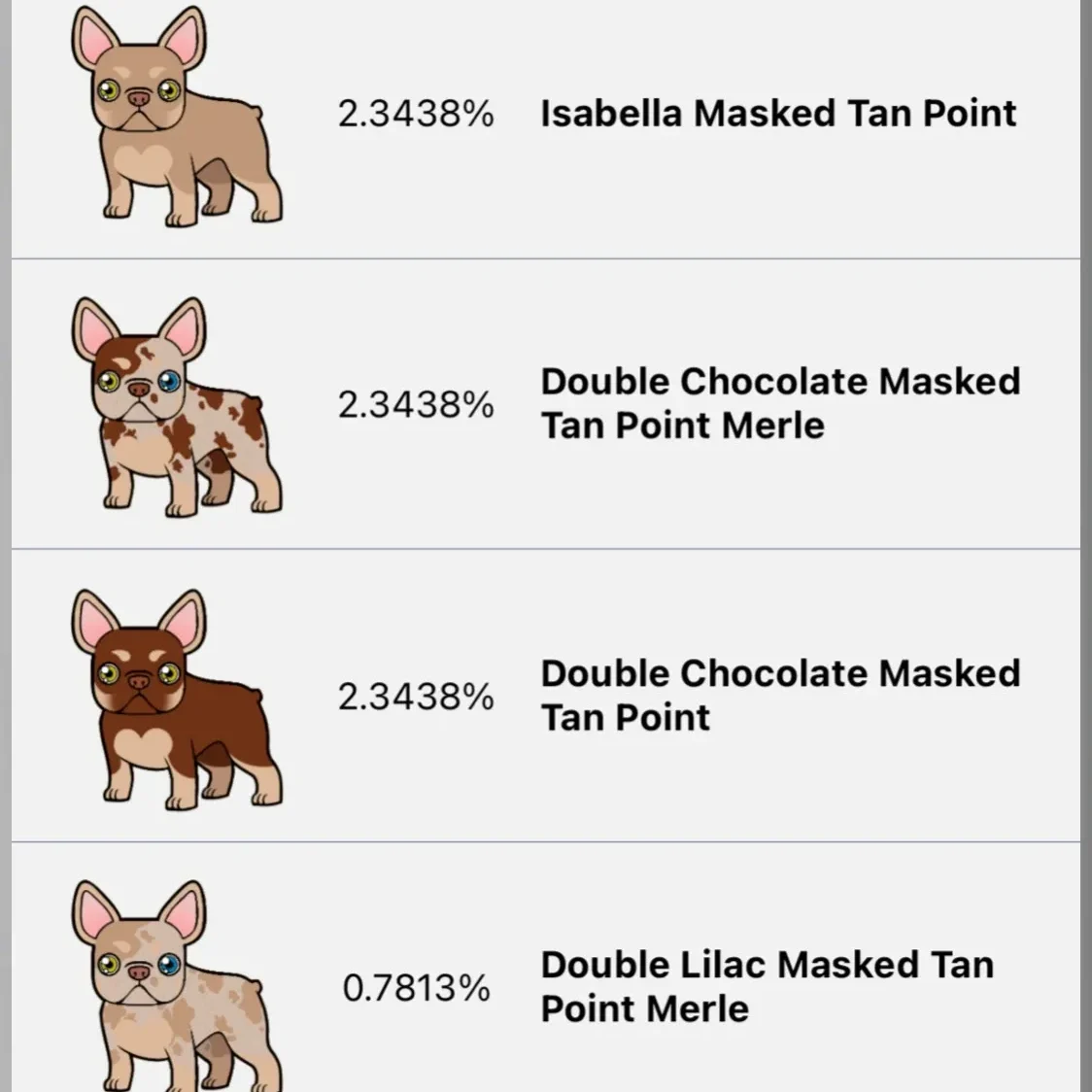
4. Avoid Undesirable Color Combinations: Certain color combinations, such as merle or double merle, can have health implications for French Bulldogs. It is important to avoid breeding dogs with these color patterns to maintain the breed’s overall health and well-being.
5. Genetic Testing: Utilize DNA testing to determine the genetic makeup of your breeding dogs. This will help identify the specific alleles and markers responsible for coat color inheritance. By testing both parent dogs, you can predict the possible color outcomes of their offspring.
6. Outcrossing: In some cases, breeders may consider outcrossing to introduce new coat colors into their breeding program. However, this should be done cautiously, taking into account the potential impact on the breed’s overall health and conformation.
7. Seek Expert Advice: Consult with experienced breeders or geneticists who specialize in French Bulldog coat colors. They can provide valuable insights and guidance on breeding strategies to achieve desired colors while maintaining the breed’s integrity.
Remember, breeding for coat color should never compromise the health or well-being of the French Bulldogs. Responsible breeding practices prioritize the overall quality and health of the breed, with coat color being just one aspect to consider.
Coat Color Changes Over Time
The coat color of a French Bulldog can change over time due to a variety of factors. One of the main factors is the presence of certain genes that control coat color. These genes can be influenced by environmental factors, such as exposure to sunlight or certain chemicals.
As a French Bulldog puppy grows and develops, its coat color can change from the color it was born with. This is because the genes responsible for coat color can become more or less active as the dog ages. For example, a puppy with a light coat color may develop a darker coat as it matures.
Coat color changes can also occur due to the natural process of shedding. As a French Bulldog sheds its puppy coat and grows its adult coat, the new coat may have a different color or pattern. This is especially true for French Bulldogs with brindle coats, as the brindle pattern can become more pronounced as the dog ages.
In addition to genetic and shedding factors, coat color changes can also be influenced by health and diet. A healthy French Bulldog with a balanced diet is more likely to have a vibrant and consistent coat color. On the other hand, a dog with health issues or a poor diet may experience dullness or changes in coat color.
It is important for French Bulldog owners to be aware of these potential coat color changes and to provide proper care and nutrition to maintain the desired color and appearance of their dog’s coat. Regular grooming, including brushing and bathing, can also help to keep the coat healthy and looking its best.
Color Inheritance Patterns

Understanding the inheritance patterns of coat color in French Bulldogs is essential for breeders and enthusiasts alike. By studying the genetic markers responsible for coat color, we can predict the likelihood of certain colors appearing in future litters.
Coat color in French Bulldogs is determined by a combination of genes inherited from both parents. These genes can be either dominant or recessive, and their interaction determines the final coat color of the offspring.
One of the most common coat color inheritance patterns in French Bulldogs is the “recessive” pattern. This means that a certain coat color will only appear if both parents carry the recessive gene for that color. For example, if both parents carry the recessive gene for a blue coat color, there is a high chance that some of their offspring will have a blue coat.
Another inheritance pattern is the “dominant” pattern, where a certain coat color will appear even if only one parent carries the dominant gene for that color. For example, if one parent has a dominant gene for a fawn coat color, there is a high chance that some of their offspring will also have a fawn coat.
Additionally, coat color inheritance can be influenced by other factors, such as the presence of certain genetic markers. These markers can modify the expression of certain genes and result in variations in coat color. By understanding these markers and their interactions, breeders can more accurately predict the coat colors of their future litters.
Overall, understanding the color inheritance patterns in French Bulldogs is crucial for breeders who want to produce specific coat colors and for enthusiasts who want to understand the genetics behind these beautiful dogs. By studying the genetic markers and testing for specific genes, breeders can make informed decisions and develop breeding strategies to achieve their desired coat colors.
Beyond Coat Color: Other DNA Factors
While coat color is an important genetic factor in French Bulldogs, there are other DNA factors that can affect their health, temperament, and overall well-being. Understanding these factors can help breeders make informed decisions and improve the breed as a whole.
1. Genetic Health Conditions
Genetic testing can identify various health conditions that French Bulldogs may be prone to. These tests can determine if a dog carries genes for conditions such as hip dysplasia, heart disease, or certain types of cancers. By identifying these genes, breeders can make better breeding choices to reduce the incidence of these conditions in future generations.
2. Temperament and Behavior
Just like humans, dogs have unique personalities and temperaments. Some French Bulldogs may be more laid-back and easygoing, while others may be more energetic and outgoing. These differences in behavior can be influenced by genetics. By understanding the DNA factors that contribute to temperament, breeders can match dogs with compatible temperaments, resulting in well-adjusted and happy puppies.
3. Physical Traits
Beyond coat color, DNA can also determine other physical traits in French Bulldogs. This includes features like ear shape, tail length, and body structure. By studying the genetic markers associated with these traits, breeders can selectively breed dogs with desired physical characteristics, improving the overall conformation of the breed.
4. Disease Resistance
Some French Bulldogs may have a higher resistance to certain diseases due to their genetic makeup. By identifying the genes associated with disease resistance, breeders can prioritize these traits in their breeding programs. This can help produce healthier puppies that are less prone to common health issues.
5. Lifespan
Genetics can also play a role in a French Bulldog’s lifespan. Certain genes may be associated with longevity, while others may increase the risk of certain age-related diseases. By understanding these genetic factors, breeders can make breeding choices that promote longer and healthier lives for their dogs.

Tyler Newsom, a canine enthusiast, is passionate about bulldogs and their coat care. With years of experience and dedication, he shares his expertise to help bulldog owners maintain their beloved pets’ fur health and vitality through practical tips and advice.
